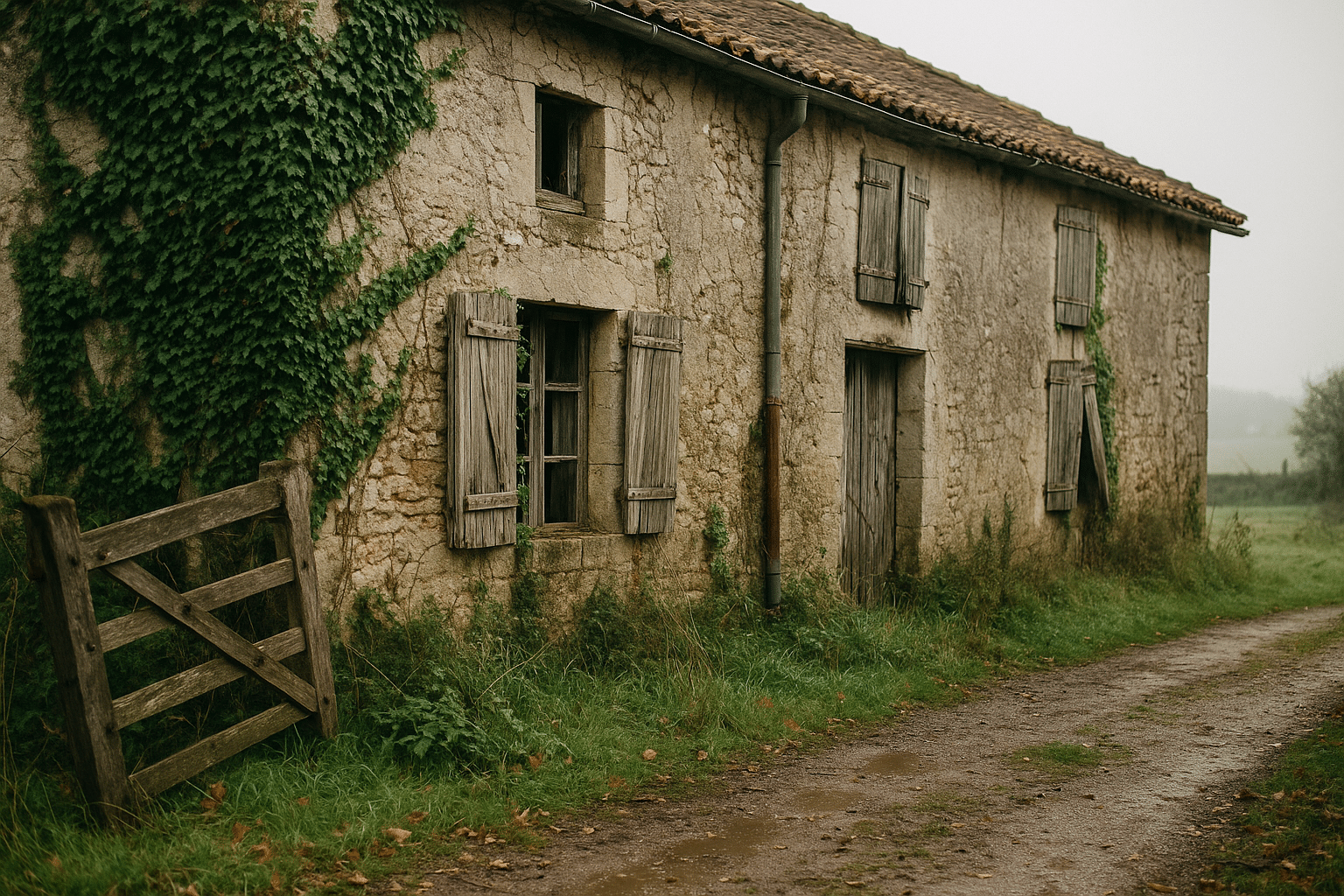
Exploring the Mysteries of Abandoned Farms
The Historical Significance of Abandoned Farms
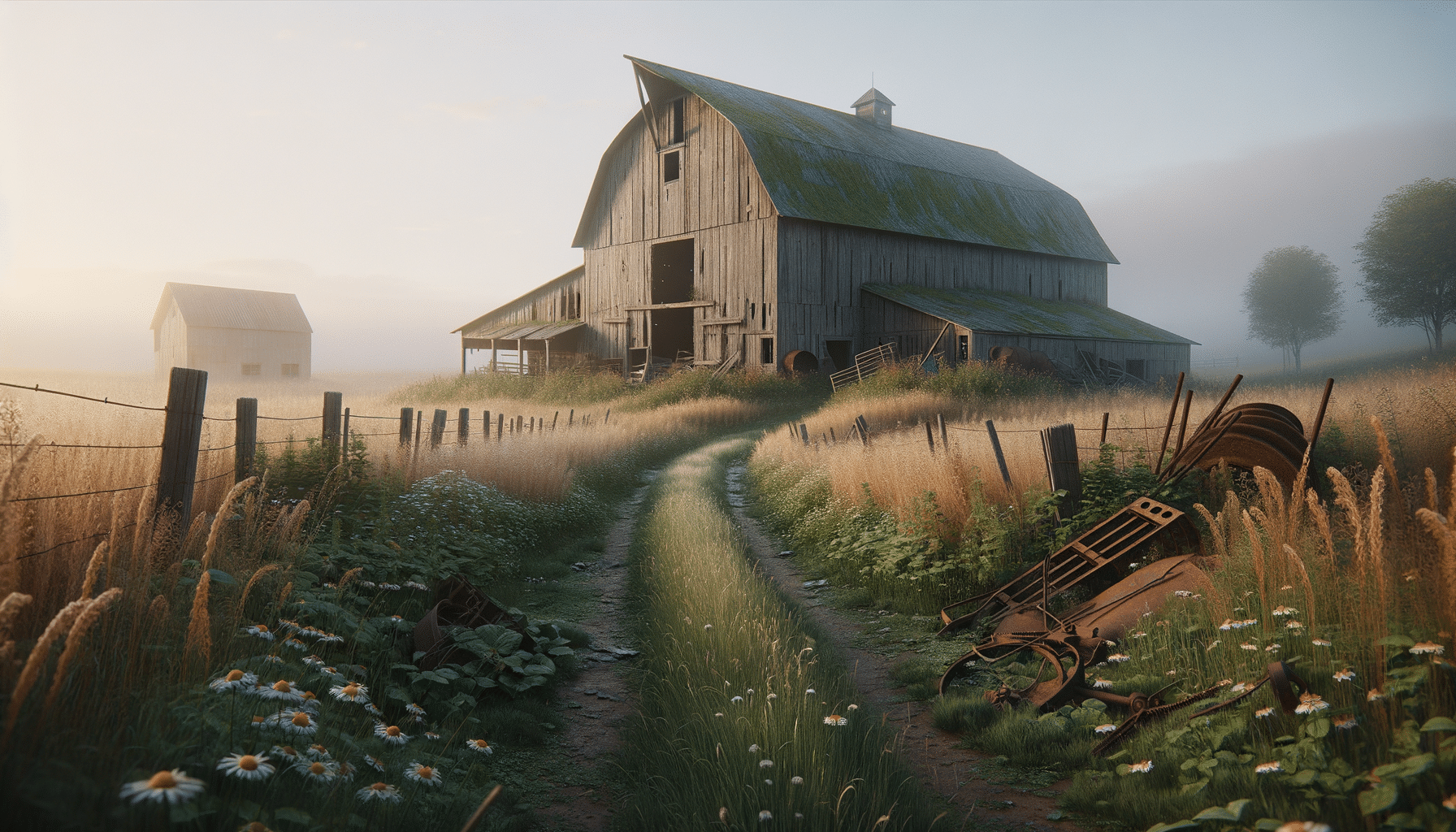
Abandoned farms are scattered across many rural landscapes, each with a tale of its own. These farms once thrived as the backbone of agricultural communities, providing sustenance and livelihoods to families for generations. Understanding the history behind these abandoned farms can offer insights into the socio-economic changes that have shaped rural areas over time.
Many of these farms were established during the agricultural boom periods, often linked to the expansion of the railroads and the promise of fertile land. However, various factors led to their decline, such as the Great Depression, which saw many farmers unable to maintain their operations. Additionally, the post-war industrial revolution shifted labor from agriculture to manufacturing, leading to the gradual abandonment of these once-bustling homesteads.
Today, these farms serve as poignant reminders of the past. They reflect the resilience and hardships of the farming families who once inhabited them. As we explore these sites, we uncover layers of history that speak of innovation, adaptation, and the inevitable march of progress.
The Environmental Impact of Abandoned Farms
While abandoned farms are often seen as relics of the past, they play a crucial role in the present-day ecosystem. When left untended, these lands can undergo significant ecological changes that impact the surrounding environment.
One of the primary environmental impacts is the rewilding of the land. As nature reclaims these spaces, abandoned farms can become havens for biodiversity. Overgrown fields and decaying structures provide habitats for various species, from insects to larger mammals. This spontaneous reforestation can enhance local biodiversity and contribute to the ecological balance.
However, there can also be negative impacts. Abandoned farms might harbor invasive species, which can outcompete native flora and fauna. Additionally, old agricultural chemicals and machinery left on-site pose risks of soil and water contamination. These challenges highlight the need for careful management and potential rehabilitation of abandoned farm sites to ensure they contribute positively to the environment.
The Cultural and Aesthetic Appeal of Abandoned Farms
Abandoned farms possess a unique aesthetic and cultural appeal that captivates artists, photographers, and historians alike. The weathered barns, rusting machinery, and sprawling fields evoke a sense of nostalgia and intrigue, inviting exploration and reflection.
These sites often become subjects for photographers and painters seeking to capture the beauty of decay and the passage of time. The contrast between the man-made structures and encroaching nature creates a visual narrative of change and resilience. For many, visiting these farms is akin to stepping into a living museum, where each artifact tells a story of its own.
Moreover, abandoned farms are rich sources of inspiration for storytelling across various media. They provide settings for novels, films, and documentaries that explore themes of loss, renewal, and the enduring human spirit. The cultural significance of these sites underscores their value beyond their historical and ecological roles.
Economic Challenges and Opportunities Related to Abandoned Farms
The existence of abandoned farms presents both challenges and opportunities from an economic perspective. On one hand, these properties can become financial burdens for local governments and communities, often requiring maintenance or restoration to prevent them from becoming hazards.
On the other hand, they offer unique opportunities for economic development. Abandoned farms can be repurposed for various ventures such as agritourism, community gardens, or even renewable energy projects. These initiatives can revitalize rural areas, providing jobs and stimulating local economies.
For instance, some communities have successfully converted abandoned farms into educational centers focused on sustainable agriculture, teaching visitors about traditional farming techniques alongside modern innovations. These projects not only preserve the cultural heritage of the area but also create sustainable economic models that benefit the wider community.
The Future of Abandoned Farms: Preservation and Innovation
Looking ahead, the fate of abandoned farms depends largely on the balance between preservation and innovation. Efforts to preserve these sites often focus on maintaining their historical integrity while exploring new uses that align with contemporary needs.
Innovative approaches to abandoned farm management include integrating technology and sustainable practices. For example, some farms are being transformed into solar farms, leveraging open spaces to generate renewable energy. Additionally, there is growing interest in using these sites for research on ecological restoration and climate change adaptation.
Preservation efforts can also involve community engagement, encouraging local participation in the restoration and maintenance of these sites. By involving communities, abandoned farms can become centers of learning and cultural exchange, fostering a sense of ownership and pride among residents.
The future of abandoned farms is not just about looking back but also about envisioning new possibilities that honor the past while embracing the potential for positive change.